Table of Contents
-
What Are HDR and SDR?
-
Three Key Differences Between HDR and SDR in LED Displays
-
How to Choose Between HDR and SDR
With the continuous advancement of display technology, LED displays have become indispensable tools in many industries. From televisions and billboards to corporate showcases, LED displays are widely used thanks to their high brightness, wide color gamut, and low power consumption. Among LED display technologies, HDR (High Dynamic Range) and SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) are two frequently mentioned key concepts. Today, we’ll dive deep into their differences to help you better understand their impact on visual performance.

1. What Are HDR and SDR?
SDR (Standard Dynamic Range):
SDR is the traditional display standard, suitable for most older display devices. It offers a limited range of brightness and contrast, meeting basic viewing needs. SDR displays provide relatively average color and brightness performance and are typically standardized based on the Rec. 709 color gamut.
HDR (High Dynamic Range):
HDR is a cutting-edge display technology that can present a wider range of brightness and more color detail. By increasing the difference in brightness and contrast, HDR makes images appear more lifelike and realistic. It supports wider color gamuts (such as Rec. 2020), enabling the display of brighter highlights and deeper shadow details.
2. Three Key Differences Between HDR and SDR in LED Displays
a. Brightness and Contrast Differences
The most intuitive difference is in brightness and contrast:
-
SDR: Traditional SDR displays usually have a peak brightness between 100 to 300 nits. The difference in brightness and contrast is relatively small, resulting in flatter image details. SDR cannot display extremely bright highlights or deep blacks, so it lacks dynamic range in light and dark scenes.
Example: When watching a standard TV program, the picture may look fine overall, but details in bright or shadowy areas—especially during scene transitions—may be lost. -
HDR: HDR technology significantly enhances display quality by providing a much higher brightness range (e.g., 1000 nits or more). In bright areas, HDR displays appear more radiant, while in dark areas, more detail is preserved, greatly enhancing image depth and immersion.
Example: When watching a 4K HDR movie, you may notice that sunlight appears more dazzling and stars in the night sky more distinct. Details are rich, and even in a dark room, you can clearly see facial expressions and object outlines.

b. Color Range Differences
Color performance is another notable distinction between HDR and SDR:
-
SDR: Traditional SDR displays can only cover a limited color space, usually following the Rec. 709 standard. This is sufficient for everyday use but cannot represent a wide range of color transitions. For example, when watching a vibrant movie or image, SDR displays might not reproduce subtle color gradations well.
-
HDR: HDR displays support much wider color gamuts (such as Rec. 2020), offering a greater variety of colors—especially in saturated and bright tones. HDR more accurately simulates real-world color differences, delivering a more lifelike visual experience.
Example: When watching a colorful nature documentary like Planet Earth on an HDR display, you’ll notice more delicate color gradations—from lush forest greens to vivid sky blues—with even subtle shadow areas realistically reproduced.

c. Application Scenarios Comparison
SDR Applications:
-
Traditional TV and Movie Playback: Most legacy TV and movie content uses the SDR standard. While it doesn’t offer the most advanced visuals, it still meets everyday entertainment needs.
-
General Office and Display Use: For most daily office work, billboards, and commercial displays, SDR screens are already sufficient.
HDR Applications:
-
High-End Home Theaters: For home cinema enthusiasts, HDR delivers a more immersive and visually stunning experience—especially when viewing 4K HDR content with enhanced detail and color depth.
-
Professional Video Production and Photography: For filmmakers, photographers, and designers, the color accuracy and detail rendering of HDR displays are essential.
-
Premium Advertising and Outdoor Displays: In outdoor advertising, HDR LED displays maintain clarity and vivid color performance even in bright sunlight, making them more eye-catching to audiences.
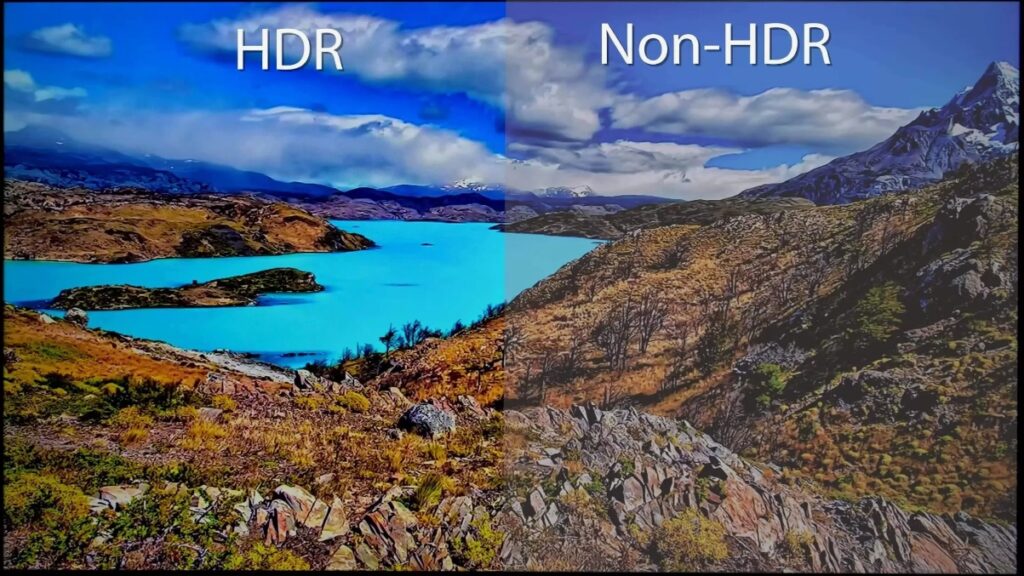

3. How to Choose Between HDR and SDR
Choosing between HDR and SDR depends on your needs and budget. While HDR offers superior brightness, contrast, and color performance, SDR displays are still more economical and sufficient for many routine applications. For example, SDR may be more practical for general television viewing or business advertising. However, if you’re aiming for a more realistic and stunning visual experience—especially for high-end home theaters or professional content production—HDR is undoubtedly the better choice.
Whether you choose HDR or SDR, the continuous improvement of LED display technology allows us to enjoy more refined and realistic visuals. As technology continues to evolve, HDR will become increasingly prevalent in various display applications.