Table of Contents
ToggleTable of Contents
-
Display Principles
-
Brightness and Viewing Angle
-
Color Performance
-
Energy Efficiency
-
Lifespan
-
Screen Thickness
-
Display Resolution
-
Installation and Maintenance
-
Cost
-
Application Scenarios
LED screens and conventional screens (LCD, OLED) represent the two major camps of modern display technology. Each has unique technical principles and application scenarios. LED screens, known for their high brightness and durability, excel in outdoor advertising and sports arenas where high brightness is required. LCD and OLED screens, on the other hand, are more commonly used in homes and offices, meeting diverse consumer demands with their thin profiles and high resolutions. This article delves into the 10 major differences between these two types of screens to help readers make wiser choices among various display technologies.
1. Display Principles
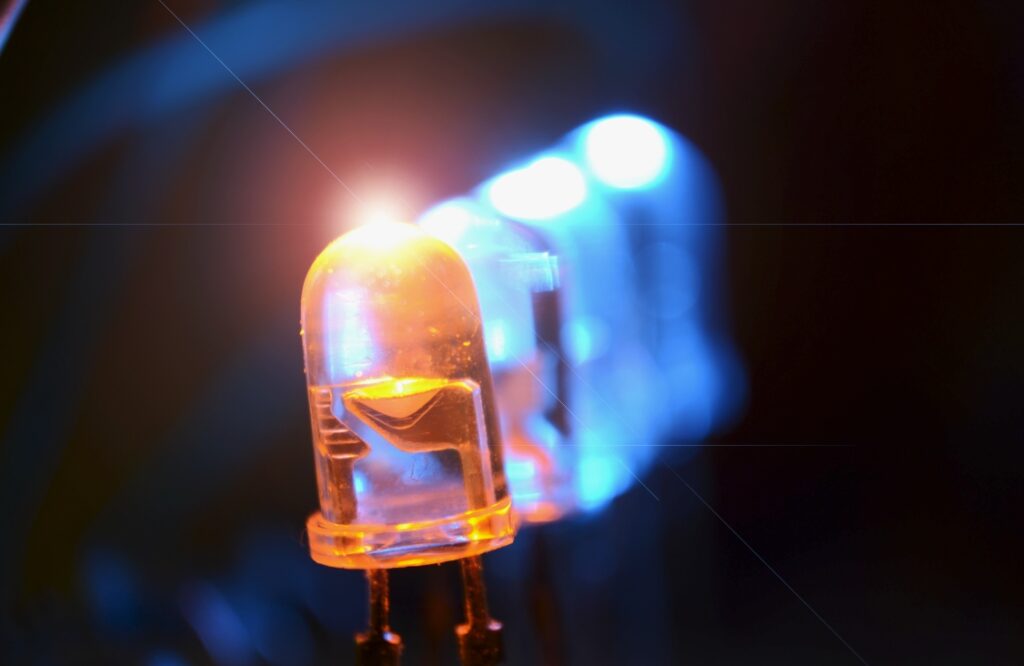
LED Screens: Use light – emitting diodes (LEDs) as the light source. They combine different – color LEDs to create images. Each LED pixel emits light independently, achieving high brightness and contrast.
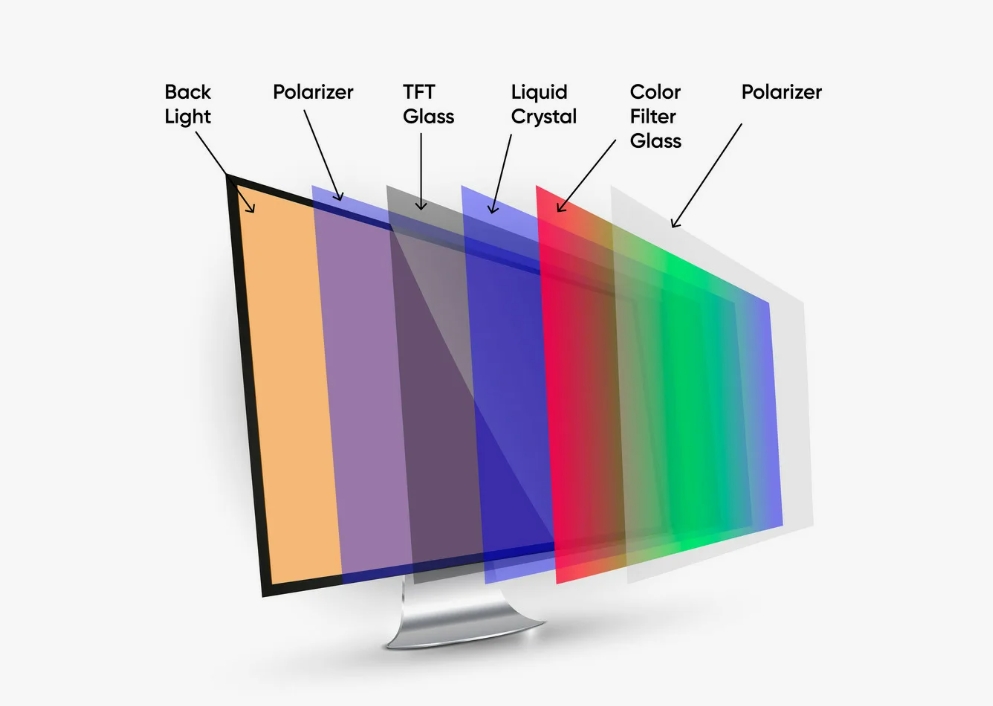
LCD Screens: Depend on liquid crystal molecules to control light transmission. They don’t emit light themselves and require a backlight (usually LED). The arrangement of the liquid crystal molecules determines the light’s transmittance, forming the image.
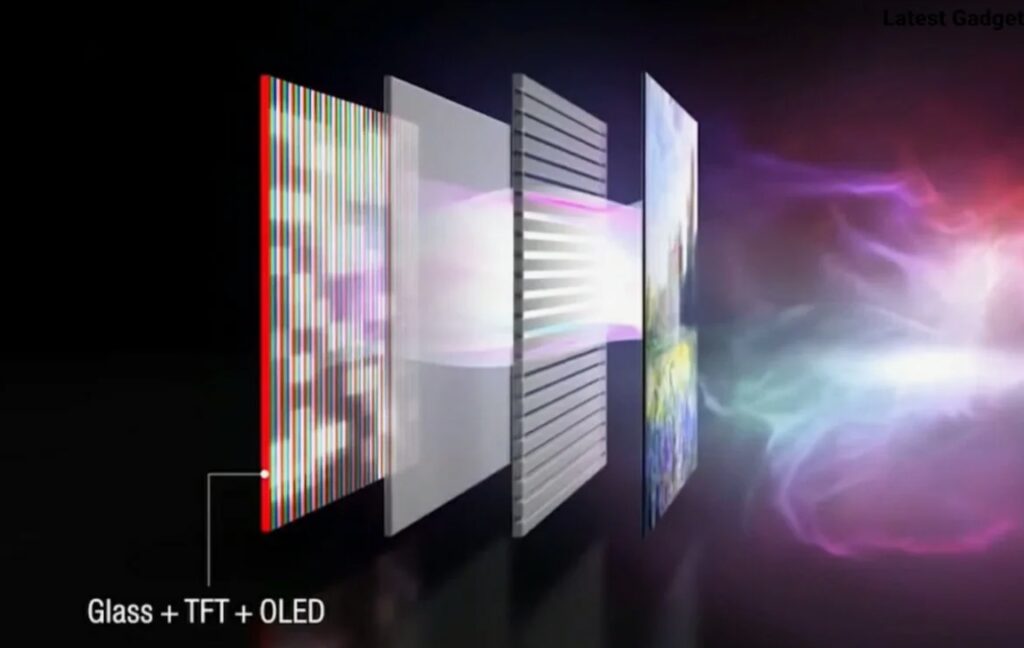
OLED Screens: Each pixel emits light by itself, using organic materials to produce light. This self – luminous characteristic allows OLED screens to achieve extremely high contrast and color saturation, with the added advantage of being thin.
Case Study: The LED screen at New York’s Times Square is a classic example of LED technology. Its high brightness and contrast make the advertisement content clear even in direct sunlight, fully demonstrating the powerful advantages of LED screens in outdoor, high – brightness scenarios.
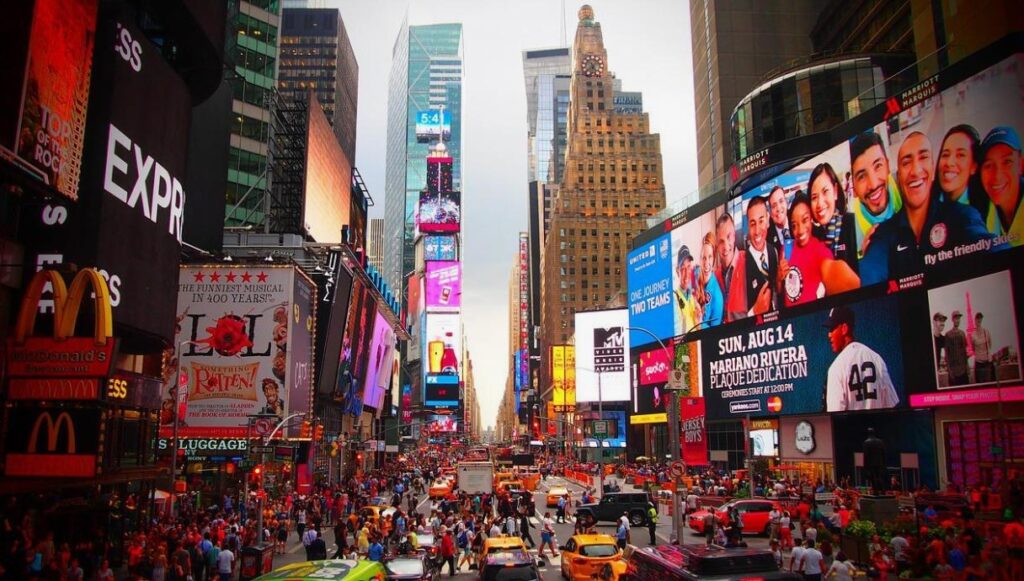

2. Brightness and Viewing Angle
LED Screens: Extremely bright, with brightness levels above 5000 nits. They are ideal for outdoor environments with strong sunlight. Also, they have a wide viewing angle, maintaining clear display effects from any angle. Here is a knowledge about nit brightness.
Conventional Screens (LCD, OLED): LCD screens have relatively low brightness, usually between 300 – 400 nits, and struggle to maintain good visibility in bright light. Although OLED screens have high contrast, their visibility in strong light is not as good as that of LED screens.

Real – World Applications: In outdoor advertising, LED screens’ high brightness and wide viewing angle make them the top choice. For example, on large – scale commercial plazas or highway billboards, LED screens ensure that the advertisement content is clearly visible under any lighting conditions, effectively enhancing the advertising effect.

3. Color Performance
LED Screens: They offer bright, vivid colors and high contrast, maintaining color vibrancy in outdoor and large – scale displays. With technological advancements, their color performance is continuously improving, meeting the display needs of various complex scenarios.
Conventional Screens: OLED screens have excellent color performance, providing high contrast and rich color layers. Their self – luminous nature allows for true black, resulting in deeper blacks and higher color saturation. In contrast, LCD screens’ color performance is limited by the backlight, with slightly inferior color brightness and contrast.

Case Comparison: LG and Samsung’s high – end OLED TVs are favored by home theater users for their outstanding color performance. These TVs can present delicate color transitions and deep blacks, offering an immersive viewing experience. In comparison, while LED screens perform well in outdoor advertising scenarios, they still need further optimization in high – color – performance scenarios like home theaters.
4. Energy Efficiency
LED Screens: They are energy – efficient, consuming less electricity and having a longer lifespan. Their energy – saving characteristics significantly reduce operational costs over long – term use.
Conventional Screens: LCD screens have relatively high power consumption, especially when high brightness is required. Although OLED screens are more energy – efficient when displaying black or low – brightness content, their power consumption significantly increases when displaying high – brightness content.
Data Support: Studies show that the energy efficiency of LED screens is usually more than 30% higher than that of LCD screens. This characteristic gives LED screens an advantage in energy – consuming outdoor advertising and large – scale display fields.
5. Lifespan
LED Screens: They have a long lifespan, typically exceeding 50,000 hours, with low maintenance costs. Their durability and stability make them ideal for long – term use environments.
Conventional Screens (LCD, OLED): LCD screens have relatively long lifespans, but OLED screens may experience “burn – in” issues. Certain images displayed for long periods can leave residual images on the screen, degrading the display quality.
Example: LED advertising screens in Guangzhou are widely used in long – term environments due to their high efficiency and long lifespan. These screens can operate stably for many years in harsh outdoor conditions, providing a reliable advertising platform for advertisers.

6. Screen Thickness
LED Screens: Generally thicker, especially in large – scale LED displays, as they require complex cooling systems to ensure stable operation.
Conventional Screens: LCD and OLED screens can be very thin, especially OLED screens. Their self – luminous technology allows for ultra – thin designs, enhancing aesthetics and saving space.
Example: Sony‘s A8H series OLED TVs, with their self – luminous technology, can achieve an ultra – thin design of only 2 – 3 millimeters, almost allowing them to be wall – mounted. This thin design not only saves space but also improves the product’s appearance.

7. Display Resolution
LED Screens: Although traditional LED displays had low resolutions, the development of small – pitch LED screens has gradually increased their resolution, even reaching 4K. These high – resolution LED screens are widely used in meeting rooms and security monitoring fields.
Conventional Screens: LCD and OLED screens usually have higher resolutions, with OLED screens capable of ultra – high resolutions, commonly used in consumer electronics like mobile phones and high – end TVs.
Technical Update: The emergence of small – pitch LED screens marks a breakthrough in LED technology for high – resolution displays. The reduction in pixel pitch allows for more detailed images, gradually approaching and even surpassing the resolution levels of traditional LCD screens. Here are the prices and purchase guides for small pitch LED displays.

8. Installation and Maintenance
LED Screens: Require complex installation and maintenance, especially large – scale LED screens, which need professional installation teams and regular maintenance. Their maintenance costs are high, but they ensure long – term stable operation.
Conventional Screens: The installation of LCD and OLED screens is relatively simple, and maintenance is more convenient, making them suitable for home users or small – scale commercial environments.
Practical Scenarios: For example, in large – scale sports arenas or outdoor advertising billboards, LED screens need regular cleaning and repair to ensure their display effects are not affected by dust and environmental factors. In contrast, LCD or OLED TVs used by home users usually only require simple cleaning and daily maintenance.
9. Cost
LED Screens: Have a high initial investment, especially for large – scale and high – resolution LED displays, which are expensive. Their high cost mainly stems from complex production processes and the demand for high – end materials.
Conventional Screens: LCD and OLED screens are relatively cheaper, especially TV and mobile phone displays, which are very popular in the consumer market and have affordable prices.
Market Comparison: The rental price of LED screens is usually high, suitable for large – scale events and exhibitions where high – quality display effects are required. In contrast, conventional displays dominate the home market and consumer – electronics product fields due to their price advantage.
10. Application Scenarios
LED Screens: Widely used in outdoor advertising, large – scale displays, shopping mall advertising, sports events, and traffic displays. Their high brightness, high contrast, and durability make them ideal choices for these scenarios.
Conventional Screens (LCD, OLED): Mainly used in homes, offices, mobile phones, TVs, and other consumer – electronics products. Their thin profiles, high resolutions, and low power consumption meet diverse consumer demands in daily use.
Conclusion
LED screens and conventional screens (LCD, OLED) each have their advantages and are suitable for different application scenarios. LED screens, with their high brightness, high contrast, and long lifespan, dominate the outdoor advertising and large – scale display fields. LCD and OLED screens, with their thin profiles, high resolutions, and low power consumption, are popular in the home, office, and consumer – electronics product markets. Understanding these differences can help users select the most suitable display technology based on their needs, achieving the best user experience.

About Dylan Lian
Marketing Strategic Director at Sostron
Dylan Lian is a seasoned LED display expert with a professional background at industry giant Leyard. Currently leading market strategy at Sostron, he has analyzed digital media needs in over 70 countries. With first-hand experience in 6,000+ global projects, Dylan bridges the gap between hardware innovation and real-world business ROI.





