Table of Contents
– LED Technology
– Basic Principles of LED Chips
– Table of LED Chip Parameters
– 9 Key Parameters of LED Chips
– 3 Application Areas of LED Chips
– 4 Development Trends of LED Chips
– Conclusion
LED Technology
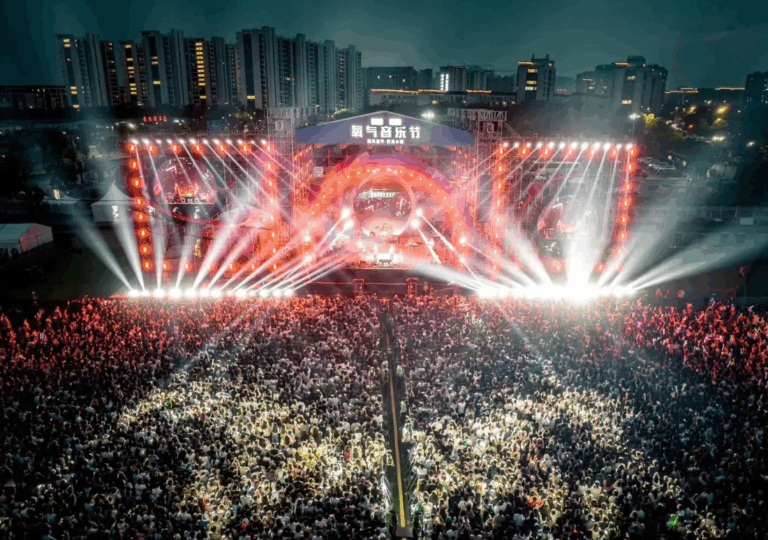
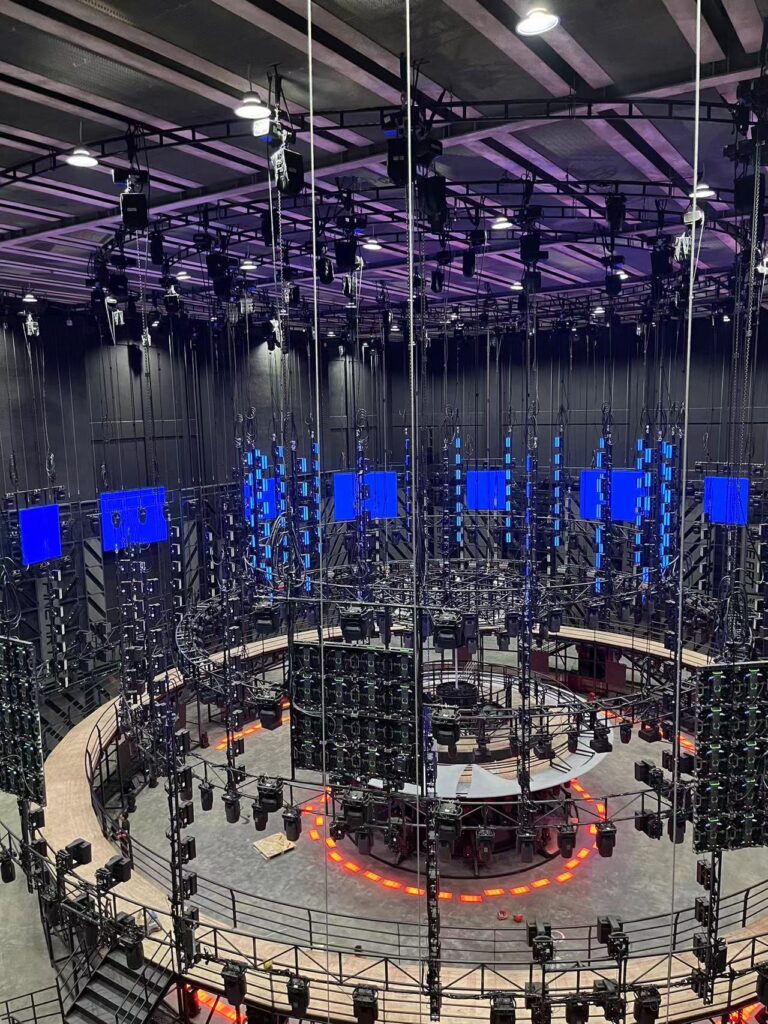
LED (Light Emitting Diode) technology, as a disruptive innovation in the field of illumination, revolves around the continuous development of LED chips. These tiny yet powerful chips are leading the lighting industry towards higher efficiency, energy-saving, and smarter directions. Here are commercial LED screen technologies, benefits and selection guide.
Basic Principles of LED Chips
LED chips are semiconductor devices that produce light by exciting solid-state emitting materials with electricity. The fundamental principle is the combination of electrons and positive holes releasing energy, which is emitted in the form of visible light. Different semiconductor materials and doping elements determine the color of the LED’s light emission. LED displays are divided into single-color, dual-color and full-color types.
Table of LED Chip Parameters
| Parameter | Typical Value |
| Luminous Efficiency | 100-200 lm/W |
| Color Temperature | 2700K – 6500K |
| Color Rendering Index (CRI) | 80-95 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to 100°C |
| Rated Current | 10-1000 mA |
| Forward Voltage | 2-4 V |
| Lifespan | 30,000-100,000 hours |
9 Key Parameters of LED Chips
1. Luminous Efficiency: The ratio of light emitted by an LED chip to the power it consumes, a crucial indicator for evaluating LED lighting efficiency.
2. Spectral Characteristics: Determine the color and distribution of light emitted by LED chips.
3. Color Temperature: Adjustable to adapt to different lighting environments.
4. Color Rendering Index (CRI): Measures the ability of LED light sources to reproduce the true colors of objects.
5. Operating Temperature: Significant for LED chip performance and lifespan, requiring effective thermal design.
6. Reverse Breakdown Voltage: Determines the safe operating range of LED chips.
7. Beam Angle: Determines the width of the LED beam.
8. Power: Related to the energy consumption and brightness of LED chips.
9. Brightness: Indicator of the light intensity emitted by LED chips.

Application Areas of LED Chips
– Illumination: LED chips find wide applications in illumination, including indoor lighting, outdoor lighting, and landscape lighting.
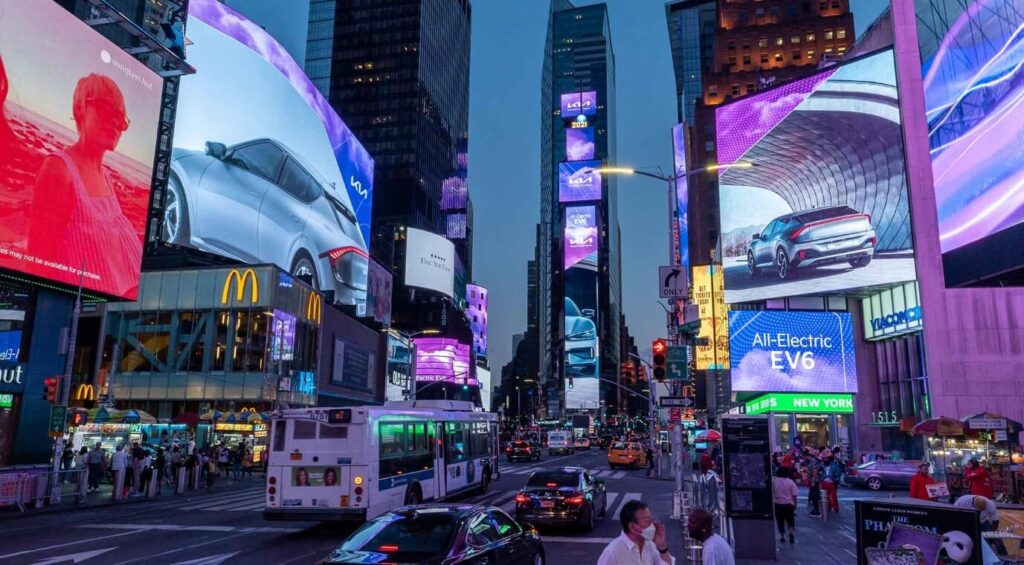
– Displays: Used in screens for televisions, computer monitors, billboards, etc. How do LED billboards work?
– Indicators: Employed in various indicators such as traffic signals, car taillights, instrument panel backlighting, etc.
Development Trends of LED Chips
– Mini LED Technology: Enhances brightness and contrast of displays by using smaller LED chips, suitable for TVs, displays, etc.
– Micro LED Technology: Further reduces the size of LED chips, enabling higher resolution and larger screen sizes, considered as the next-generation display technology.
– Smart Lighting: Features such as dimmability, adjustable color temperature, remote control, etc., to meet the personalized and intelligent lighting needs of users.
– Material Innovation: Introduction of new materials leads to significant progress in LED chip efficiency, stability, and reliability.
Conclusion
LED chips, as the core components of LED lighting products, have extensive application prospects and significant market potential. With continuous technological advancements and expanding applications, LED chips will continue to develop towards high power, multifunctionality, environmental friendliness, intelligent control, and flexibility. In the future, as smart and IoT technologies become more widespread, LED chips will integrate more closely with various application scenarios, providing humanity with more intelligent, efficient, and eco-friendly lighting experiences.





